dBµV – logarithmic voltage unitdBµV – absolute level unit relative to 1 µV (microvolt). The unit is commonly used in the radio, DVB-T and satellite technology.
|
Example: satellite signal meter, DVB-T signal meter: input level range in dBµV,antenna amplifiers and multi-switches: input and output level range in dBµV.
|
The unit expressed in dBµV indicates how much lower or higher the voltage is relative to 1µV. 0 dBµV corresponds to 1 µV (microvolt).
|
The following voltage equation is used to convert µV into dBµV: 
|
U(ref) – reference value, i.e. reference unit, in this case 1 µV
|
To simplify, the equation for voltage in dBµV is: 
|
Example:
Converting 11.22 µV into dBµV. 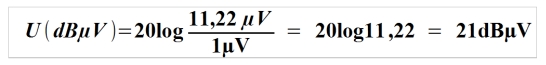
|
The following equation is used to convert dBµV into µV: 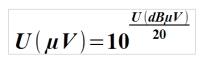
|
Example:
Converting 51 dBµV into µV (microvolts). 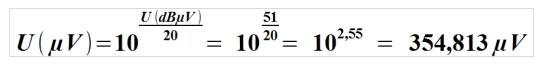
|
Table 1. Converting signal level from dBµV to voltage in µV and mV | Signal level in dBµV | Voltage in µV | Voltage in mV | | 0 | 1 | 0,001 | | 3 | 1,413 | 0,014125 | | 6 | 1,995 | 0,0019953 | | 9 | 2,818 | 0,0028184 | | 12 | 3,981 | 0,0039811 | | 15 | 5,623 | 0,0056234 | | 18 | 7,943 | 0,0079433 | | 21 | 11,220 | 0,011 | | 24 | 15,849 | 0,016 | | 27 | 22,387 | 0,022 | | 30 | 31,623 | 0,032 | | 33 | 44,668 | 0,045 | | 36 | 63,096 | 0,063 | | 39 | 89,125 | 0,089 | | 42 | 125,893 | 0,126 | | 45 | 177,828 | 0,178 | | 48 | 251,189 | 0,251 | | 51 | 354,813 | 0,355 | | 54 | 501,187 | 0,501 | | 57 | 707,946 | 0,708 | | 60 | 1000 | 1 | | 63 | 1412,538 | 1,413 | | 66 | 1995,262 | 1,995 | | 69 | 2818,383 | 2,818 | | 72 | 3981,072 | 3,981 | | 75 | 5623,413 | 5,623 | | 78 | 7943,282 | 7,943 | | 81 | 11220,185 | 11,220 | | 84 | 15848,932 | 15,849 | | 87 | 22387,211 | 22,387 | | 90 | 31622,777 | 31,623 | | 93 | 44668,359 | 44,668 | | 96 | 63095,734 | 63,096 | | 99 | 89125,094 | 89,125 | | 102 | 125892,541 | 125,893 | | 105 | 177827,941 | 177,828 | | 108 | 251188,643 | 251,189 | | 111 | 354813,389 | 354,813 | | 114 | 501187,234 | 501,187 | | 117 | 707945,784 | 707,946 | | 120 | 1000000 | 1000 |
|
The voltage can be easily converted into power: dBµV and dBmV to dBm. However, the internal impedance must be known to convert power to voltage. DVB-T, cable or industrial television systems use 75 Ohm impedance. Radio systems use 50 Ohm impedance.
|
Equations for those two environments are given below:
|
dBm = dBµV – 106,98 (@ 50 ohm)
dBm = dBµV – 108,75 (@ 75 ohm)
|
Example:
Converting 70 dBµV to dBm (at 75 Ohm)
|
dBm = 70 – 108,75 = –38,75 dBm
|
dBm = dBmV – 46,9897 (@ 50 ohm)
dBm = dBmV – 48,7506 (@ 75 ohm)
|
Example:
Converting 60 dBmV to dBm (at 75 Ohm).
|
dBm = 60 – 48,7506 = 11,2494 dBm,
|
which is approx. 11.25 dBm.
|
Relationship between dBmV and dBµV:
|
|
 New products
New products