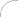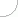Dielectric
Dielectrics include all materials that do not conduct electricity. The electric charges present in any solid, cannot move freely in dielectrics (unlike conductors). |
Basic materials used as dielectrics include |
Air is also an insulator. Remember, that the insulating properties decrease with the increase in moisture. |
In daily life, dielectrics are widely used in cable technology. Regardless of the type and application of the cable, its conductors must be insulated, which requires use of plastics, usually thermosetting or thermoplastic. The insulation material is selected depending on the application of the cable. |
For high voltage power cables, the insulation material must show high break-down immunity, low permittivity and fault tolerance. It should also maintain its properties both at low and high temperatures. |
Dielectrics are also key components used in coaxial cables (Fig. 1). Dimensions and dielectric constant also determine the wave impedance of the cable. |
Fig. 1. Cross section of NS100 Delta coaxial cable (outer sheath [A] is the main cable insulation; the inner conductor is protected by a physically expanded dielectric [B]) |